| [1] Sibai T,Morgan EF,Einhorn TA.Anabolic agents and bone quality.Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469(8):2215-2224.[2] 田野.运动生理学高级教程[M].北京:高等教育出版社,2003:844-858.[3] Frost HM.A 2003 update of bone physiology and Wolff’s Law for clinicians.Angle Orthodontist.2004;74(1):3-15.[4] Frost HM.Wolff’s Law and bone’s structural adaptations to mechanical usage: An overview for clinicians.Angle Orthodontist.1994;64(3): 175-188.[5] 朱欢,李荣娟,李峰,等.长期气排球运动对绝经后妇女骨密度的影响[J].湖北师范学院学报:自然科学版,2016,36(1):50-53.[6] 沈华.不同形式的健身运动和体成分对中老年女性骨密度的影响[J].成都体育学院学报,2008,34(12):71-74.[7] Nordstrom P,Pettersson U,Lorentzon R.Type of physical activity,muscle strength,and pubertal stage as determinants of bone mineral density and bone area in adolescent boys.J Bone Miner Res. 1998;13(7):1141-1148.[8] Nikander R,Sievanen H,Heinonen A,et al.Femoral neck structure in adult female athletes subjected to different loading modalities.J Bone Miner Res.2005;20(3):520-528.[9] Heinonen A,Oja P,Kannus P,et al.Bone mineral density of female athletes in different sports. Bone Miner.1993;23(1):1-14.[10] Heinonen A,Oja P,Kannus P,et al.Bone mineral density in female athletes representing sports with different loading characteristics of the skeleton.Bone.1995;17(3):197-203.[11] 姚鑫,罗琳,洪邦辉,等.太极拳运动对老年男性骨质疏松患者锻炼情绪及骨密度和生理指标的影响[J].贵州师范大学学报:自然科学版, 2016,34(3): 32-36.[12] Hinton PS,Nigh P,Thyfault J.Effectiveness of resistance training or jumping-exerciseto increase bone mineral density in men with low bone mass: A 12 -month randomized,clinical trial.Bone. 2015;79: 203-212.[13] 陈志斌,邓小林.太极拳和篮球运动对老年人骨代谢影响的比较[J].体育学刊,2002,5(11):31-32.[14] 刘佑民,仪刚勤.不同运动项目对骨密度的影响[J].绍兴文理学院学报, 2015,35(10):116-120.[15] 伍贤平,廖二元,刘忠厚.不同国家和地区各种族人群骨密度参考值及其相互比较[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2007,13(1):1-21,36. [16] 黄陈恕,吴景全,朱艳琳. 重庆地区中老年男性骨质疏松症患者骨密度与年龄、身高、体质量、体质量指数关系研究[J].四川医学, 2016,37(7): 717-720.[17] 魏秋实,陈镇秋,谭新,等.中国男性和女性血清25羟维生素D水平与年龄、性别和骨密度之间的关系[J].实用骨科杂志, 2016,22(5):480.[18] 徐国昌,张庆远,徐飞,等.河南回族成人四肢骨量和骨密度与肢体长宽度的年龄变化及相关性调查研究[J].中国全科医学, 2016,19(15):1818-1823.[19] [No authors listed]Prevention and management of osteoporosis.World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser.2003;921:1-164.[20] 郭盖,李梦阳.体育专业和非体育专业男性大学生骨密度与体成分的对比研究[J].运动,2015,3:58-60.[21] 葛男,宋相勳,宋信穎.12周篮球运动训练对肥胖男大学生身体成分和骨骼密度影响的研究[J].曲阜师范大学学报, 2014,40(3):92-97.[22] James MM, Carroll S.Progressive high-intensity resistance training and bone mineral density changes among premenopausal women. Sports Medicine.2006; 36(8) :683-704.[23] lima F,Falco V De,Baima J,et al.Effect of impact load and active load on bonemetabolism and body composition of adolescent athletes.Med Sci Sports Exerc.2001;33(8):1318-1323.[24] 李天乐.太极拳练习对男性中老年体成分和睾酮及骨密度影响的研究[D].宁波:宁波大学体育学院学,2015.[25] Sherv VD,Palmer IJ,Bemben MG,et al.Relationships between body composition,muscular strength,and bonemineral density in estrogen deficient postmenopausal women.Clin Densitiom.2009;12(3):292-298.[26] 赵立君,李凤丽,陈琼,等.篮球专业和非篮球专业男性大学生身体不同部位骨密度对比分析[J].吉林大学学报:医学版, 2007,33(6):1077-1079. [27] 杨欣,郑淑蓉,陈荣京,等 北京地区青年峰值骨密度与遗传因素的相关性分析[J].中华妇产科杂志,2003,38(5):273-276. [28] 王簕,林启旺,白玉玲,等.氧化应激和骨代谢水平与老年原发性骨质疏松症间的相互关系[J].中国骨质疏松症杂志, 2015,21(2):192-195,202. [29] Cann CE, Martin M,Genant HK,et al.Decreased spinal mineral content in amenorrheic women. JAMA.1984;251(5):626-629.[30] 王峰.关于降钙素降低骨质疏松性骨折发病率的临床分析[J].中国实用医药,2015,10(2):163-164.[31] Turner AG,Anderson PH,Morris HA.Vitamin D and bone health.J Clin Lab Invest Suppl.2012;243(4):65-72.[32] Yoon V,Maalouf NM,Sakhaee K.The effects of smoking on bone metabolism.Osteoporos Int.2012;23(8):2081-2092.[33] Polymeris A,Michalakis K,Sarantopoulou V.Secondary underlying mechanisms.Endocr Regul.2013;47(3):137-148.[34] 李宝新,周雪,梁璇璇,等.老年男性2型糖尿病合并抑郁患者骨代谢指标与骨密度变化[J].中国医学前沿杂志:电子版, 2015,7(12):17-20. [35] 吴新炎,陈月亮,李芙蓉.我国篮球儿童少年后备人才骨密度研究[J].湖北理工学院学报:人文社会科学版,2016,33(3):83-88. [36] 梁芝栋.大学生篮球运动员和普系学生的指长比均值比较[J].体育学刊, 2017,24(2):135-139.[37] 姜鑫.基于皮纹学视角构建中国汉族女篮选材体系的研究[J].体育科技, 2014,35(6): 68-73. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
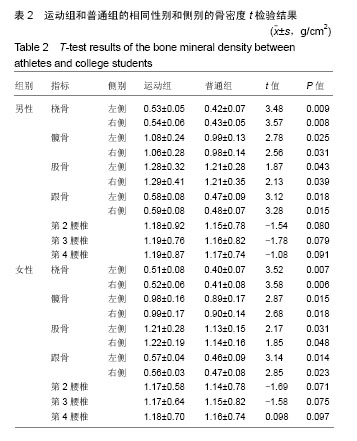
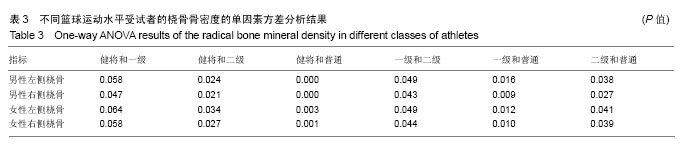

.jpg)